FEA analysis of Pressure Vessel
Problem Definition
By examining the structural reaction to internal pressure, this study attempts to determine if ASTM A36 steel is suitable for use in pressure vessels. Important goals are to identify the kind of cylinder (thick or thin), calculate longitudinal and hoop stresses at burst pressure, determine the maximum pressure (burst pressure) using a Factor of Safety (FOS) of 2, and compare these results with analytical calculations. Taking into account a FOS of 2, the investigation will also look at the dimensional changes in diameter and length at maximum internal pressure.
Objectives
- Determine if the pressure vessel is a thick or thin cylinder.
- With a FOS of 2, find the highest pressure (burst pressure) that the vessel can tolerate.
- At burst pressure, calculate the longitudinal and hoop stresses for the cylinder and spherical shell, and compare the results with analytical calculations.
- Determine the change in diameter and length that results from the highest internal pressure while taking a FOS of 2 into account.
Material Properties
ASTM A36 steel
Physical density : 7.85 g/cc
UTS of Material : 400MPa
Yield strength : 250MP
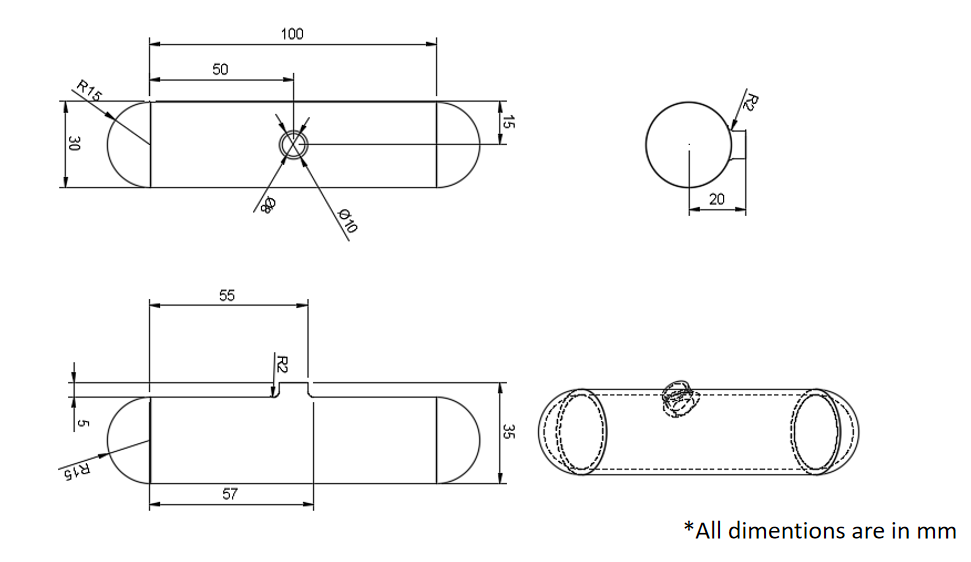
Geometry
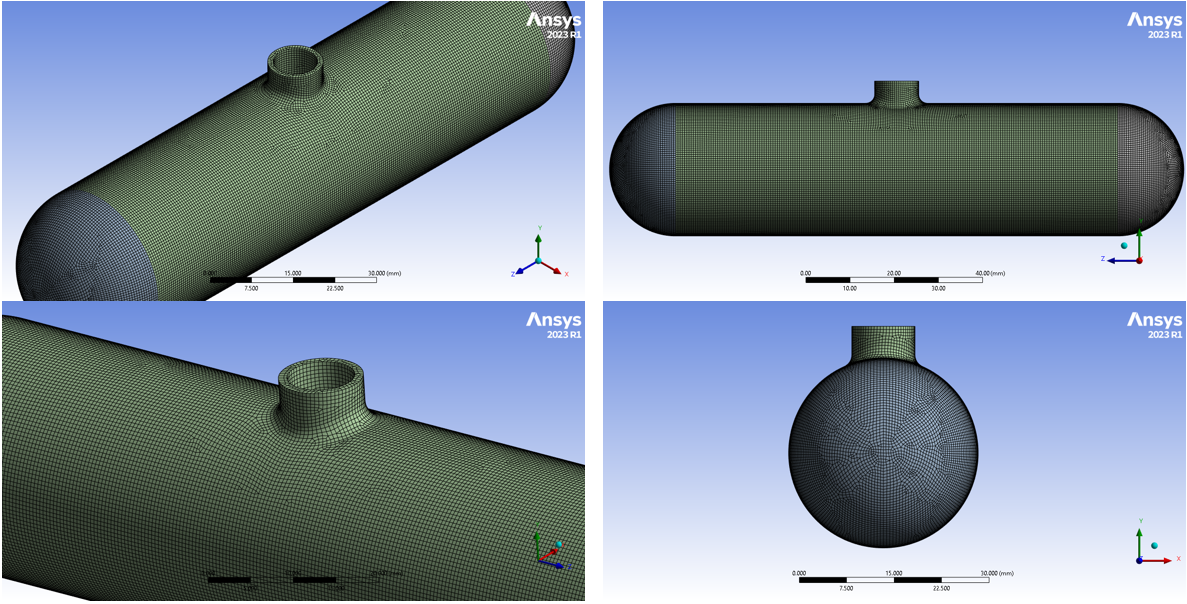
Generated Mesh
Nodes : 1056854
Elements : 256125
Task-1 : Predict if the cylinder is thick or thin cylinder?
The pressure vessels are identified as thick or thin by the ratio of the mean radius of the vessel to the thickness of the wall.
A vessel is considered to be thin walled if the value of this ratio is greater than 10, and if it is below 10, the vessel is called a thick cylindrical vessel.
13/4 = 3.25
3.25<10 …(thick cylinder vessel)
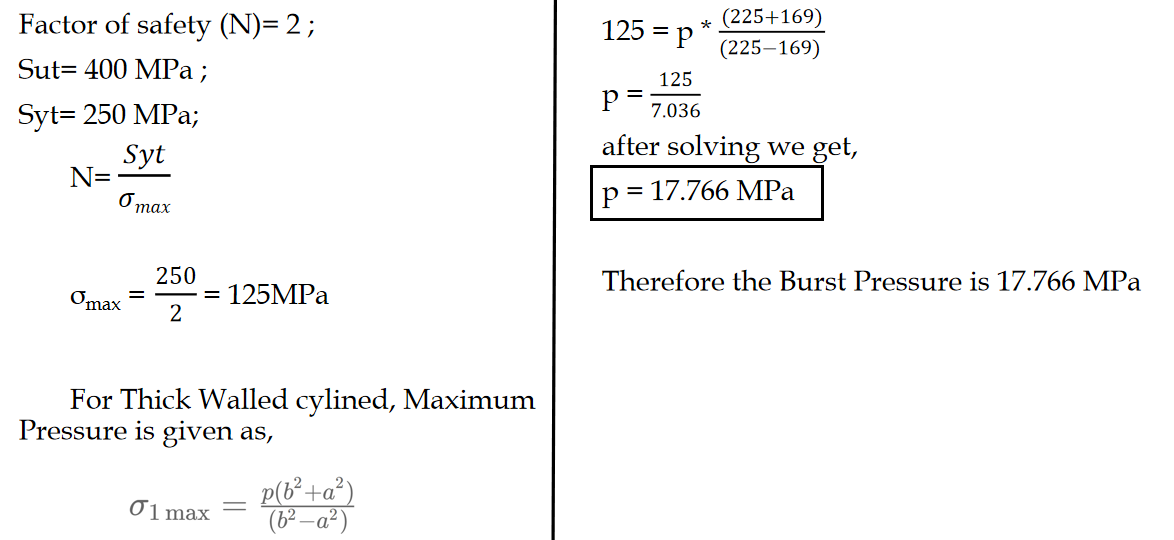
Task-2: Maximum pressure that the vessel can withstand (burst Pressure)
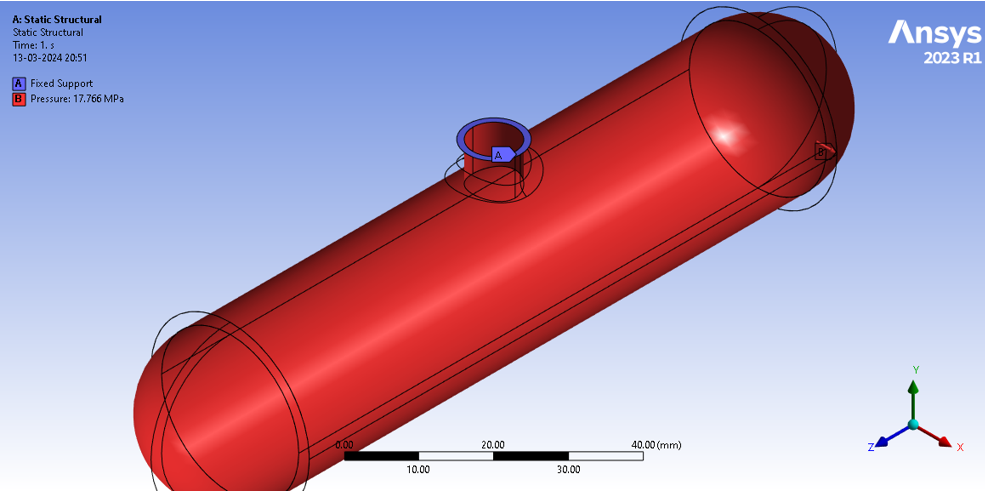
Boundary Conditions
Results
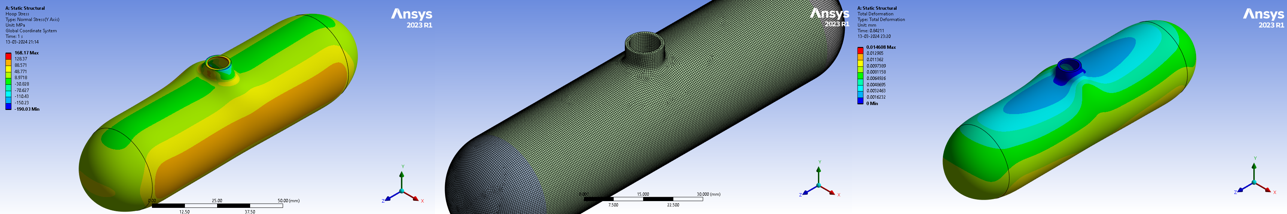
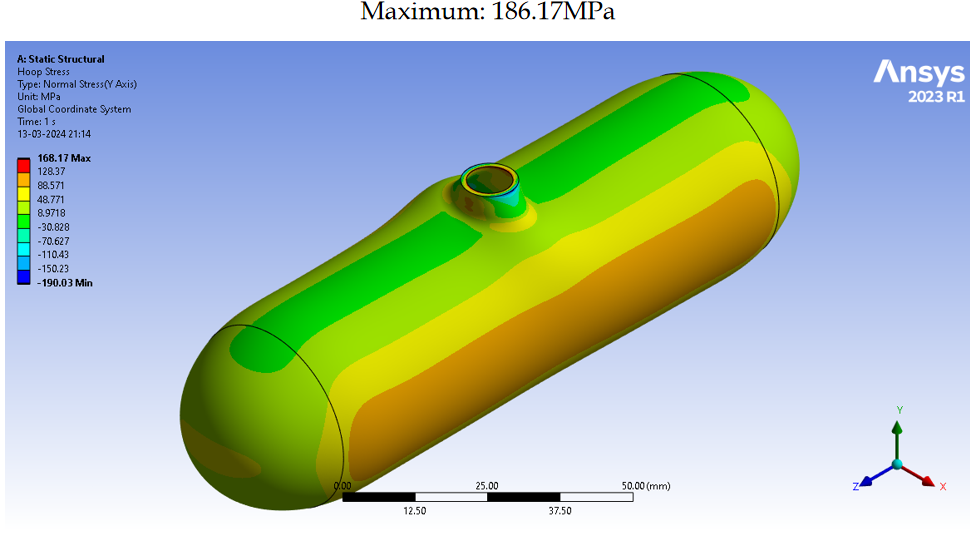
Hoop Stress
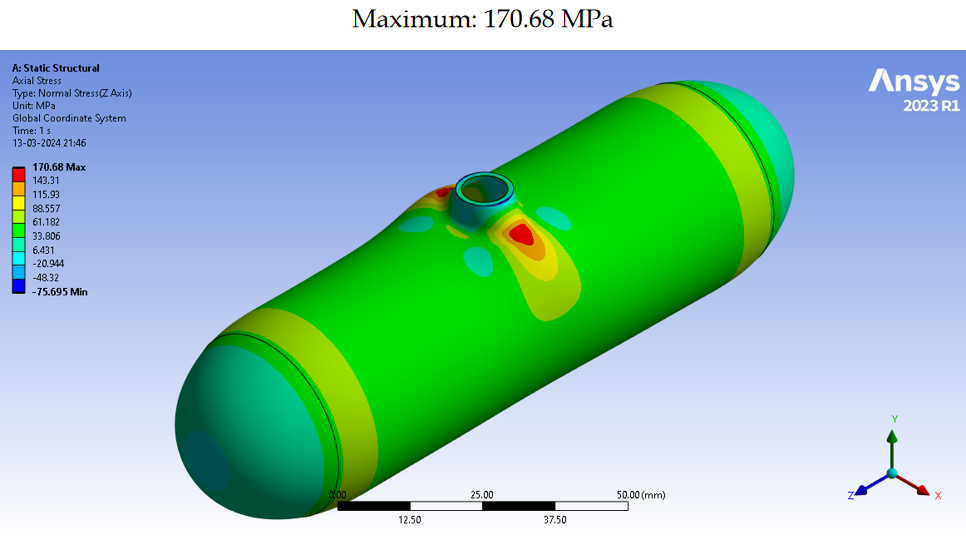
Longitudinal Stress
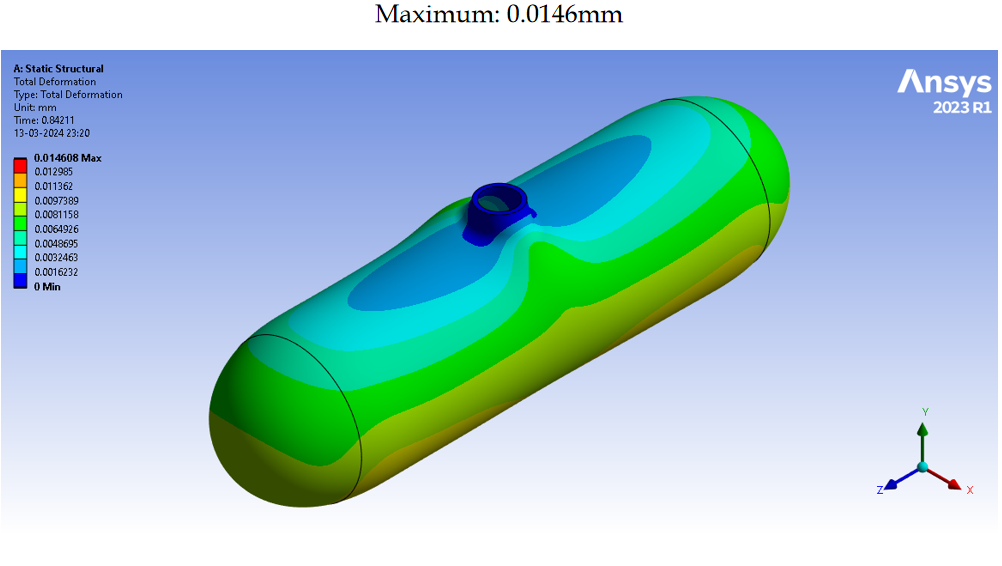
Deformation
Analytical Solution

Conclusion
The Finite Element Analysis (FEA) of the thick pressure vessel indicates a factor of safety of 2, meeting the design requirement for safe operation.
The vessel's burst pressure is calculated to be 17.766 MPa, satisfying the safety margin criterion.
Maximum hoop stress: 186.17 MPa, well below the material's ultimate tensile strength (UTS) of 400 MPa.
Maximum longitudinal stress: 170.68 MPa, within the material's yield strength of 250 MPa.
Post a comment